The State of Kuwait (Arabic: دولة الكويت, pronounced [dawlat̪ alkuwajt̪]) is a sovereign Arabemirate bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and Iraq to the north and west. The name is adiminutive of an Arabic word meaning "fortress built near water."[4] It has a population of 3.1 million and an area of 17,818 km². Kuwait is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government, with Kuwait City serving as the country's political and economic capital.
In 1990, Kuwait was invaded and annexed by neighboring Iraq. The seven month-long Iraqi occupation came to an end after a direct military intervention by United States-led forces. Nearly 750 Kuwaiti oil wells were set ablaze by the retreating Iraqi army resulting in a major environmental and economic catastrophe.[5] Kuwait's infrastructure was badly damaged during the war and had to be rebuilt.[6]
Kuwait has the world's fifth largest oil reserves[7] and is the fourth richest country in the world per capita.[8] Kuwait's oil fields were discovered and exploited in the 1930s. After it gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1961, the nation's oil industry saw unprecedented growth. Petroleum and petroleum products now account for nearly 95% of export revenues, and 80% of government income.[9] Kuwait is regarded as the most developed country in theArab League and a Major non-NATO ally of the United States.
Contents[hide] |
[edit]History
In 4th century BC, the Ancient Macedonians colonized the island, Failaka, on today's Kuwait coast under Alexander the Great and named it "Ikaros".[10]
Recorded history of the State of Kuwait goes back to the year 1613. [11] Tribes from centralArabia settled in Kuwait in the 17th-century after experiencing a massive drought in their native land. Kuwait used to be a major center for spice trading between India and Europe. By late 18th-century, most of the local people made a living selling pearls. In 1756, the people elected Sabah I bin Jaber as the first emir of Kuwait. [12] The current ruling family of Kuwait,al-Sabah, are descendants of Sabah I.
During the rule of the Al-Sabah, Kuwait progressively became a center of trade and commerce. It now served as a hub of trade between India, the horn of Africa, the Nejd,Mesopotamia and the Levant. Up until the advent of Japanese pearl farming, Kuwait had one of the largest sea fleets in the Persian Gulf region and a flourishing pearling industry. Trade consisted mainly of pearls, wood, spices, dates and horses.
As the influence of the Ottoman Empire increased in the region, Kuwait was assigned the status of a caza of the Ottomans. After the signing of the Anglo-Ottoman Convention of 1913, then emir of Kuwait, Mubarak Al-Sabah, was diplomatically recognized by both the Ottomans and British as the ruler of the autonomous caza of the city of Kuwait and the hinterlands.[13]The 1922 Treaty of Uqair set Kuwait's border with Saudi Arabia and also established the Saudi-Kuwaiti neutral zone, an area of about 5,180 km² adjoining Kuwait's southern border. Oil was first discovered in Kuwait in the 1930s and the government became more proactive in establishing internationally recognized boundaries. After World War I, the Ottoman Empire was financially crippled and the invading British Indian Armyinvalidated the Anglo-Ottoman Convention, declaring Kuwait to be an "independent sheikdom under British protectorate".
On 19 June 1961, Kuwait became fully independent following an exchange of notes between the United Kingdom and the then emir of Kuwait,Abdullah Al-Salim Al-Sabah.[13] The Gulf rupee, issued by the Reserve Bank of India, was replaced by the Kuwaiti dinar. The discovery of largeoil fields, such as the Burgan field, triggered a large influx of foreign investments into Kuwait. The massive growth of the petroleum industry transformed Kuwait into one of the richest countries in the Arabian Peninsula and by 1952, the country became the largest exporter of oil in thePersian Gulf region. This massive growth attracted many foreign workers, especially from Egypt and India. Kuwait settled its boundary disputes with Saudi Arabia and agreed on sharing equally the neutral zone's petroleum reserves, onshore and offshore. After a brief stand-off over boundary issues, Iraq formally recognized Kuwait's independence and its borders in October 1963. During the 1970s, the Kuwaiti government nationalized the Kuwait Oil Company, ending its partnership with Gulf Oil and British Petroleum. In 1982, Kuwait experienced a major economic crisis after the Souk Al-Manakh stock market crash and decrease in oil price.[14] However, the crisis was short-lived as Kuwait's oil production increased steadily to fill the gap caused by decrease in Iraq's and Iran's oil production levels following the events of the Iran–Iraq War. In 1983, aseries of six bomb explosions took place in Kuwait killing five people. The attack was carried out by Shiite Dawa Party to retaliate Kuwait's financial support to Iraq during its war with Iran.[15]
Kuwait had heavily funded Iraq's eight year-long war with Iran. After the war ended, Kuwait declined an Iraqi request to forgive its US$65 billion debt.[16] An economic warfare between the two countries followed after Kuwait increased its oil production by 40 percent.[17] Tensions between the two countries increased further after Iraq alleged that Kuwait was slant drilling oil from its share of the Rumaila field.[17]
On 2 August, 1990 Iraqi forces invaded and annexed Kuwait. Saddam Hussein, then President of Iraq, deposed the emir of Kuwait, Jaber Al-Sabah, and installed Ali Hassan al-Majid as the new governor of Kuwait.[18] After a series of failed diplomatic negotiations, the United States-led coalition of thirty-four nations fought the Persian Gulf War to remove the Iraqi forces from Kuwait. On February 26, 1991, the coalition succeeded in driving out the Iraqi forces, restoring the Kuwaiti emir to power.[19] Kuwait paid the coalition forces US$17 billion for their war efforts.[19]
During their retreat, the Iraqi armed forces carried out a scorched earth policy by damaging 737 oil wells in Kuwait, of which approximately 600 were set on fire.[20] It was estimated that by the time Kuwait was liberated from Iraqi occupation, about 5 to 6 million barrels (950,000 m3) of oil was being burned in a single day because of these fires.[21] Oil and soot accumulation had affected the entire Persian Gulf region and large oil lakes were created holding approximately 25 to 50 million barrels (7,900,000 m3) of oil[22] and covering 5% of Kuwait's land area.[20] In total, about 11 million barrels (1,700,000 m3) of oil was released into the Persian Gulf[23] and an additional 2% of Kuwait's 96 billion barrels (1.53×1010 m3) of crude oil reserves were burned by the time the oil fires were brought under control.[24] The fires took more than nine months to extinguish fully and it took Kuwait more than 2 years and US$50 billion in infrastructure reconstruction to reach pre-invasion oil output.[25] Kuwait has since largely recovered from the socio-economic, environmental, and public health effects of the Persian Gulf War.
[edit]Politics
Kuwait is a constitutional monarchy and has the oldest directly elected parliament among the Arab states of the Persian Gulf. The head of state is the Emir or Sheikh, a hereditary office. A council of ministers, also known as cabinet ministers, aids the Prime Minister in his task as the head of Government of Kuwait which must contain at least one elected member of the Kuwaiti parliament, known as Majlis Al-Umma (National Assembly). The National Assembly has the power to dismiss the Prime Minister or any member of cabinet through a series of constitutional procedures. All cabinet ministers are answerable to the National Assembly.[26]
The National Assembly consists of fifty elected members, who are chosen in elections held every four years. Government ministers are also granted membership in the parliament and can number up to sixteen excluding the fifty elected members. According to the Constitution of Kuwait, nomination of a new Emir or Crown Prince by the ruling Al-Sabah family has to be approved by the National Assembly. If the nominee does not win the votes of the majority of the assembly, the royal family must submit the names of three other candidates to the National Assembly, and the Assembly must approve one of them to hold the post. Any amendment to the constitution can be proposed by the Emir but it needs to be approved by more than two-thirds of the members of the National Assembly before being implemented.[27] There have been several conflicts between the Emir, the government and the National Assembly over various policies. The National Assembly was suspended from 1976 to 1981, from 1986 to 1991 and from May 1999 to July 1999 due to irresolvable conflicts between some members of the government and the Assembly.[26] The Assembly was dissolved again in May 2009 by the Emir leading to the resignation of Prime Minister Sheik Nasser Mohammad al-Ahmad al-Sabah and the rest of the Cabinet.[28] Nationwide elections were held on May 16 2009.[29]
More than two-thirds of those who reside in Kuwait do not hold Kuwaiti citizenship and thus cannot vote in parliamentary elections. Additionally, prior to 2005, only 15% of the Kuwaiti citizen population was allowed to vote, with all "recently naturalized" citizens (i.e. those of less than thirty years' citizenship), and members of the Kuwaiti Armed Forces excluded. On 16 May 2005, Parliament permitted women's suffrage by a 35-23 vote, subject to official interpretation of Islamic law and effective for the 2006 parliamentary election.[30] The decision raised Kuwait's eligible voter population from 139,000 to about 339,000. In 2006, Kuwaiti citizens were estimated to be more than 960,000. In 2005, the former Prime Minister Sheikh Sabah al-Ahmad al-Sabah announced the appointment of the first women as a cabinet minister, Massouma Mubarak. She was designated the post of Planning Minister and Minister of State for Administrative Development Affairs.[31] During the 2008 parliamentary elections, 27 of the 275 candidates were women. However, none of them won.[32] In the parliamentary elections on 16 May 2009, 16 female candidates contested for 50 seats for a four-year term. Four female candidates won their seats and became Kuwait's first female lawmakers.[33]
[edit]Geography and climate
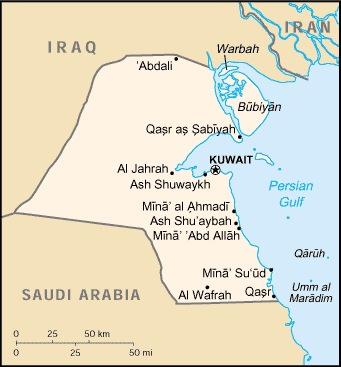
Located in the north-east corner of the Arabian Peninsula, Kuwait is one of the smallest countries in the world in terms of land area. The flat, sandy Arabian Desert covers most of Kuwait. There is little difference in the country's altitude with the highest point in the country being 306 m above sea-level.[9] It has nine islands, all of which with the exception of Failaka Island are uninhabited.[34] With an area of 860 km², theBubiyan is the largest island in Kuwait and is connected to the rest of the country by a 2,380 m long bridge.[35] The land area is considered arable[9] and sparse vegetation is found along its 499 km long coastline.[9] Kuwait City is located on Kuwait Bay, a natural deep-water harbor.
Kuwait has some of the world's richest oil fields with the Burgan field having a total capacity of approximately 70 billion barrels (1.1×1010 m3) of proven oil reserves. During the 1991 Kuwaiti oil fires, more than 500 oil lakes were created covering a combined surface area of about 35.7 km².[36] The resulting soil contamination due to oil and soot accumulation had made eastern and south-eastern parts of Kuwait uninhabitable. Sand and oil residue had reduced large parts of the Kuwaiti desert to semi-asphalt surfaces.[21] The oil spills during the Persian Gulf War also drastically affected Kuwait's marine resources.[37]
Kuwait has a hyper-arid continental climate.[38] Summer, which lasts from May to September, is extremely hot and dry with temperatures easily crossing 45 °C (113 °F) during daytime, with temperatures usually around 52 °C at midday.[39] Kuwait has a fairly high day-night temperature range. Winter, from November through February, is cool with some precipitation and average temperatures around 13 °C (56 °F) with extremes from -2 °C to 27 °C. Annual rainfall averages less than 127 mm (5 in.) and occurs chiefly between October and April.[40] The spring season in March is warm and pleasant with occasional thunderstorms. The frequent winds from the northwest are cool in winter and spring and hot in summer. Southeasterly winds, usually hot and damp, spring up between July and October; hot and dry south winds prevail in spring and early summer. The shamal, a northwesterly wind common during June and July, causes dramatic sandstorms.[40]
[edit]Governorates
Kuwait is divided into six governorates (muhafazat, sing. muhafadhah):
The governorates are subdivided into districts.
The major cities are the capital Kuwait City and Jahrah (a thirty-minute drive northwest of Kuwait City). The main residential and commercial areas are Salmiya and Hawalli. The main industrial area is Shuwaikhwithin the Al Asimah Governorate. The main palace is the As-Seef Palace in the old part of Kuwait City where the Emir runs the daily matters of the country whilst the government headquarters are in the Bayan Palace and the Emir lives in Dar Salwa.
[edit]Economy
Kuwait has a GDP (PPP) of US$138.6 billion[41] and a per capita income of US$60,800,[41] making it the fourth richest country in the world.[8] Kuwait's human development index (HDI) stands at 0.912, the second highest in Middle East, after Israel and the highest in the Arab world. With a GDP growth rate of 5.7%, Kuwait has one of the fastest growing economies in the region.[41] According to the 2008 Index of Economic Freedom, Kuwait has the second-most free economy in the Middle East.[42] In March 2007, Kuwait's foreign exchange reserves stood at US$213 billion.[43] The Kuwait Stock Exchange, which has about 200 firms listed, is the second-largest stock exchange in the Arab world with a total market capitalization of US$235 billion.[44] In 2007, the Kuwaiti government posted a budget surplus of US$43 billion.[45]
Kuwait has a proven crude oil reserves of 104 billion barrels (15 km³),[41] estimated to be 10% of the world's reserves. According to the Kuwaiti constitution, all natural resources in the country and associated revenues are government property.[46] Being a tax-free country, Kuwait's oil industry accounts for 80% of government revenue. Petroleum and petrochemicals accounts for nearly half of GDP and 95% of export revenues. Increase in oil prices since 2003 resulted in a surge in Kuwait's economy.[47] Kuwait's current oil production of 2.8 million bpd is expected to increase to 4 million bpd by 2020.[48] To realize this production target, Kuwait Petroleum Corporation plans to spend US$51 billion between 2007 to 2012 to upgrade and expand the country's existing refineries.[49] However, the country's economy was badly affected by theglobal financial crisis of 2008.[50] In 2009, the Central Bank of Kuwait devised a US$5.15 billion stimulus package to help boost the economy.[51]
Other major industries include shipping, construction, cement, water desalination, construction materials and financial services.[41] Kuwait has a well developed banking system and several banks in the country date back to the time before oil was discovered. Founded in 1952, the National Bank of Kuwait is the largest bank in the country and one of the largest in the Arab world.[52] Other prominent financial institutions based in Kuwait include the Gulf Bank and Burgan Bank, which is named after the largest oilfield in the country. Kuwait's climate limits agricultural development. Consequently, with the exception of fish, it depends almost wholly on food imports. About 75% of potable water must be distilled or imported. The government is keen on decreasing Kuwait's dependence on oil to fuel its economy by transforming it into a regional trading and tourism hub. The planned US$77 billion City of Silk is the largest real estate development project in the Middle East.[43] The Central Bank issues Kuwait’s currency, the Kuwaiti dinar. In December 2007, the dinar was the highest valued currency unit in the world.[53]
In 2007, estimated exports stood at US$59.97 billion and imports were around US$17.74 billion. Petroleum, petrochemical products, fertilizersand financial services are major export commodities. Kuwait imports a wide range of products ranging from food products and textiles to machinery. Kuwait's most important trading partners are Japan, United States, India, South Korea, Singapore, China, European Union and Saudi Arabia.[41] Japan is the largest customer of Kuwaiti oil followed by India, Singapore and South Korea.[54]










0 comments:
Post a Comment